Builder#
Deploy from GitHub#
From the KubeSail dashboard under Repos, click Connect New Repository, and select which repo you want to install the KubeSail DeployBot. You can grant access to selected repositories within the user or organization’s account.
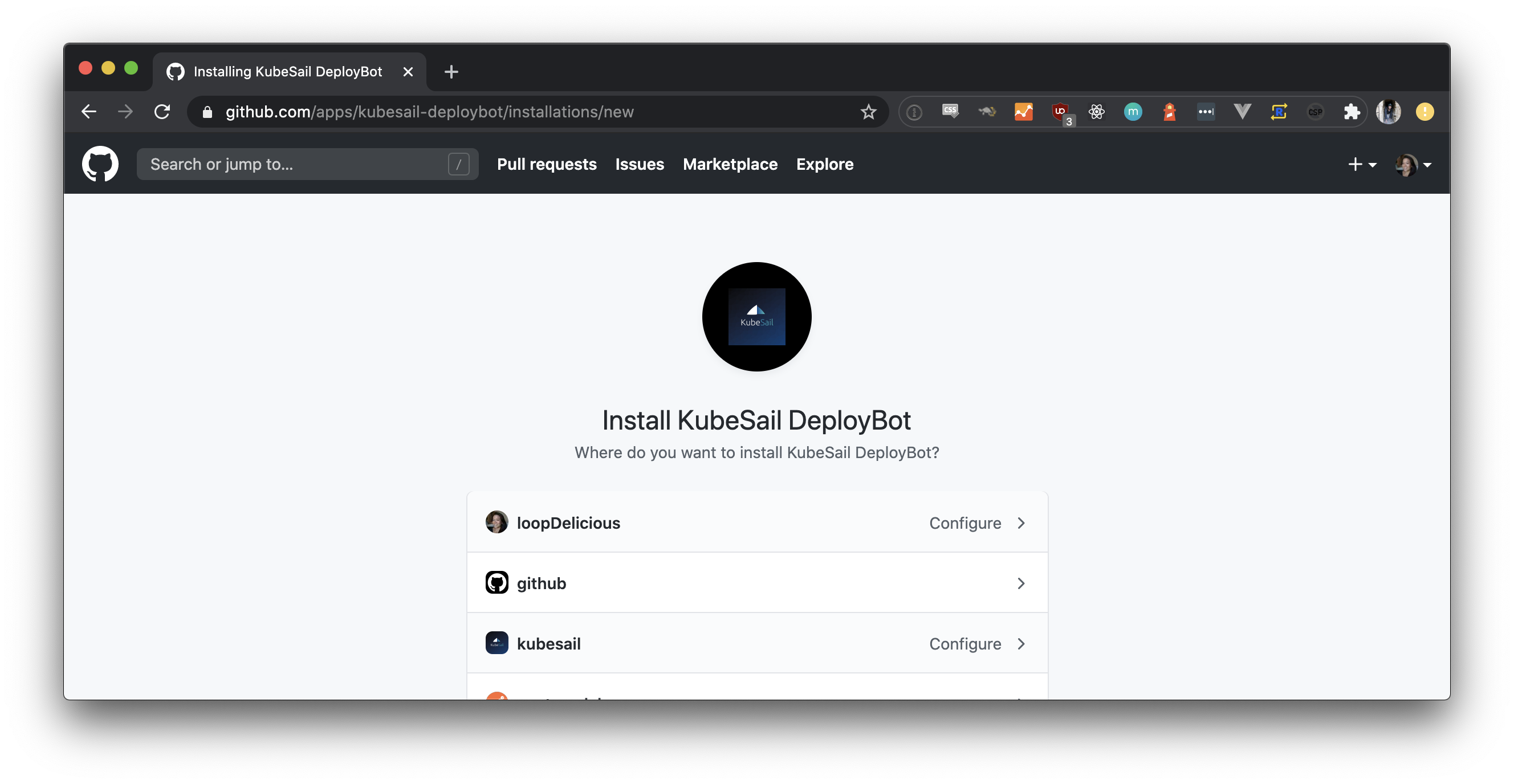
Once you grant KubeSail access to a GitHub repository, it appears under Repos within the KubeSail dashboard.
Select the newly added repository to view the suggested pipeline. Pick a branch to build and a Kubernetes context from the dropdowns, and then click Build Now. You can view the build logs beneath your pipeline.
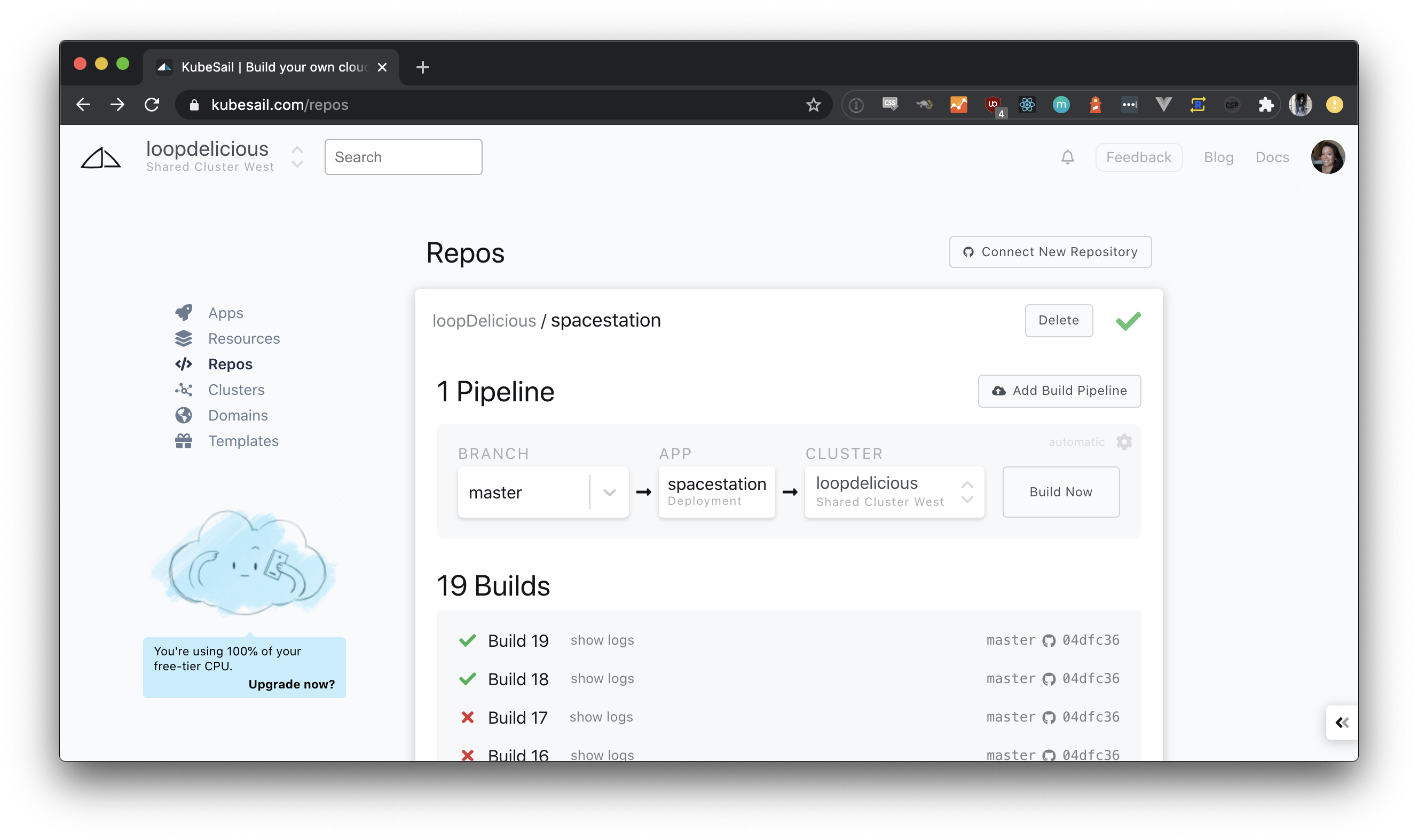
Once your app successfully builds and deploys, it appears under Apps within the KubeSail dashboard.
What does Builder build?#
The Builder uses deploy-node-app under the hood, our tool for deploying projects to Kubernetes. The repo builder will prompt you a number of times during the first build to answer some questions about how to build your project. For the simplest use-case, simply create a Dockerfile!
Deployment options#
Learn how to deploy simple HTML, Node.js, Python, and Ruby on Rails apps onto Kubernetes.
- Create a Dockerfile
- Build and push your Docker image
- Deploy your app on any Kubernetes cluster
A static site#
If npx deploy-node-app is called in a directory with nothing but an “index.html” file, it will still work! An Nginx server with your static site will be generated and ready in a few seconds.
Node.js#
npx deploy-node-app will generate (if missing) a Dockerfile, build and push deployment images, generate Kubernetes configurations files, and trigger a deployment on your Kubernetes cluster.
npx deploy-node-app
This tool generates all the boilerplate required for container-based deployments on Kubernetes or Docker.
- Create a Dockerfile if none exists
- Create a Kubernetes Deployment or
docker-compose.yamlfile - Automatically map ports from Docker to your Node app
- Build and push your Docker image
- Deploy your app on any Kubernetes cluster
If you don’t have an existing Node app, KubeSail created create-node-app as an easy way to bootstrap a new app with React, Express, Postgres, and Redis.
npx create-node-app my-node-app
Python#
Create a Dockerfile for Python#
- Create an image containing your Python application by placing a file called
Dockerfilein the root of your project. - Update the line with
your-daemon-or-script.py.
FROM python:3
WORKDIR /usr/src/app
COPY requirements.txt ./
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir -r requirements.txt
COPY . .
CMD [ "python", "./your-daemon-or-script.py" ]
Then, continue on to build and push your Docker image.
Ruby on Rails#
Create a Dockerfile for Rails#
- Create an image containing your Ruby on Rails application by placing a file called
Dockerfilein the root of your project.
FROM ruby:2.5
RUN apt-get update -qq && apt-get install -y nodejs postgresql-client
RUN mkdir /myapp
WORKDIR /myapp
COPY Gemfile /myapp/Gemfile
COPY Gemfile.lock /myapp/Gemfile.lock
RUN bundle install
COPY . /myapp
EXPOSE 3000
# Start the main process.
CMD ["rails", "server", "-b", "0.0.0.0"]
Then, continue on to build and push your Docker image.
Build your Docker image#
Run the following command with username being your Docker Hub username.
docker build . -t username/your-image-name
docker push username/your-image-name
Deploy your app to KubeSail#
Once you’ve built your image and pushed to Docker Hub, you can deploy your app to KubeSail. Update the image section of the config below, and then apply your updates using kubectl.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: your-app
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: your-app
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: your-app
spec:
containers:
- name: your-app
image: username/your-image-name
imagePullPolicy: Always
ports:
- name: listen-port
containerPort: 8080
resources:
requests:
cpu: 10m
memory: 128Mi
limits:
cpu: 1
memory: 256Mi